Guide to Passivation & Conversion Coating
In this guide, DEK provides the metal surface finishing- passivation definition, applications, advantages as well as even more.
What is Passivation & Conversion covering?
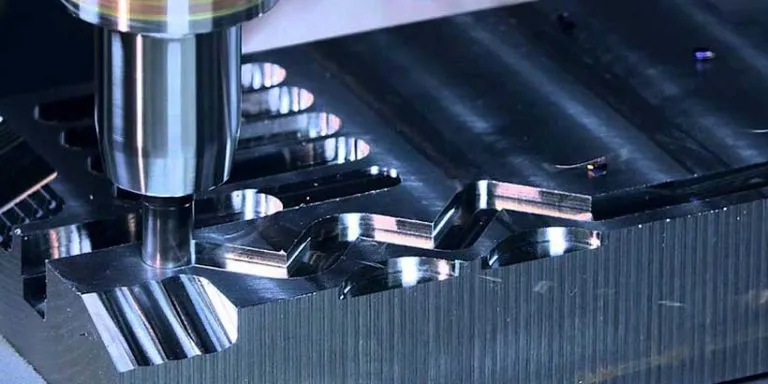
Passivation is a surface finishing technique frequently executed after CNC machining, it’s a chemical therapy for stainless steel and various other metals to remove ferrous contaminants or use a light coat of safety product to produce a covering for improving the deterioration resistance or lowering the chemical sensitivity. Passivation procedure only takes place in particular conditions.
Conversion coatings are covering for metals converted to a protective layer through the chemical or electrochemical processes. Passivation/Conversion Covering procedure consisting of Anodizing, Bluing, Plasma electrolytic oxidation, Chromate conversion layer, Phosphate conversion coating.
Why make use of Passivation?
After CNC machining or manufacturing, welding, handling as well as other processes, the manufacture particles, tramp iron, and surface impurities will leave on the components, which jeopardizing the natural ability to withstand the corrosion of metals like stainless steel, while passivation can eliminate the pollutants from the surface area as well as update the surface properties.
Passivation Applications
- Semiconductor sector, the surface passivation procedure makes semiconductor surface render inert and also does not transform semiconductor properties.
- Products made from stainless steel and also other self-passivating alloys.
- Aerospace and also army industries, to enhance the top quality and precision of aeroplane and also armed forces parts.
- The medical industry, guarantee the sanitation procedure.
- Silicon, nickel, ferrous materials, and so on.
The Benefits of Passivation
- Boosts rust resistance
- Lower the risk of product contamination
- Reduces upkeep for metal products
- Keep the integrity of metal performance
- The passivation process consists of a strict cleaning stage